Scientific knowledge provides robust evidence about human motivation, emotional intelligence, and effective leadership, showing us how to create better, healthier, and more productive workplaces. However, this knowledge is often not systematically applied in daily organisational practice. As a coach and DEIB practitioner, I am dedicated to exploring methodologies for translating empirical findings into practical strategies that address the complex demands of everyday working environments. Contact me via email if I can be of service to you or your organisation.
What do you think?
Many critical human skills are often undervalued and rarely taught. For example, how do you navigate difficult conversations? How do you communicate effectively? How do you give and receive feedback constructively? Beyond that, we need to train coping mechanisms and stress management, especially the ability to ask for help. Whether in a personal or professional context, I think you’ll be better equipped to thrive when you have the confidence to say, “I’m struggling, can you help me?”
The crucial link
I think a lot of what we do is learned behaviour.
Society tells us, "Be yourself," but then turns around and says, "No, not like that.”
Society says, "Tell me how you feel," but only if those feelings are comfortable or convenient. If your authenticity makes others uncomfortable, they reject it.
““The courage to be is the courage to accept oneself, in spite of being unacceptable.””
Step up your expectations
Image c/o Shutterstock ©
The Pygmalion Effect is also known as the Rosenthal Experiment, named after a research of Robert Rosenthal at Harvard, in his famous "Oak School" experiment in 1968. It’s a psychological phenomenon in which an individual's performance is influenced by the expectations placed upon them by others. This concept is rooted in the idea that beliefs and expectations can shape reality.
When high expectations are set, individuals are more likely to feel motivated and supported, which fosters greater effort and persistence. These expectations are often communicated unconsciously through subtle cues such as tone of voice, body language, or the level of attention and encouragement provided. I think positive expectations tend to enhance performance, creating a self-fulfilling prophecy that reinforces the initial belief.
Facing adversity
© Erhui1979 c/o Getty Images
When facing adversity, we often hear the advice to "let it go." I think this phrase can be misleading and unhelpful, instead, the focus should be on "letting it be." Understanding the difference between these two approaches is crucial for building mental strength and resilience. "Letting it go" is one of the hardest concepts to grasp in psychology, where it is known as cognitive dismissal. This process involves attempting to forget or dismiss painful memories and emotions. However, as humans, we are wired to remember pain and significant experiences. These memories are programmed into our minds, and trying to erase them can feel almost impossible. In contrast, "letting it be" focuses on cognitive acceptance. This approach involves acknowledging and accepting our emotions and experiences without trying to force them away. By allowing ourselves to sit with these feelings, we can process them more effectively and integrate them into our lives in a healthier way.
Building mental muscles
c/o Lund University
Mental strength is not about repressing or denying our emotions. I think it’s about knowing the right strategies to use in order to navigate difficult situations. This is akin to "building mental muscles." Just as we go to the gym to lift weights and build physical strength, we must also engage in practices that build our mental resilience. Some practical strategies include mindfulness meditation, journaling, self-compassion, seeking support, and setting boundaries. By embracing cognitive acceptance and employing strategies to build mental resilience, we can navigate adversity more effectively and emerge stronger. Remember, mental strength is not about denying our pain but about knowing how to handle it with grace and wisdom.
Help or hindrance
One of my favourite principles in psychology is the cognitive dissonance theory. It suggests that we often perceive people in ways that align with our existing stereotypes, rather than seeing them as they truly are. In other words, we interpret reality through the lens of what we think is there, not necessarily what is there. This has significant implications for leadership.
Clear expectations
Human beings are deeply motivated by their social standing within groups. Recognition and acknowledgment are powerful tools to elevate an individual’s status, activating the brain's reward system, which encourages positive behaviours. Research shows that when people feel recognised, they are more likely to be engaged and supportive in their roles. On the other hand, uncertainty can trigger defensive behaviours as the brain perceives it as a threat. Providing clarity and predictability helps to reduce anxiety and create psychological safety. I think this allows individuals to focus on collaboration rather than self-protection, boosting performance and engagement.
Control the narrative
“The Courage to Be Disliked" is a popular self-help book by Ichiro Kishimi and Fumitake Koga that explores the concept of embracing our true selves and living authentically, even if that means being disliked by others. The book is based on the principles of Alfred Adler's psychology and offers practical advice on how to develop the courage to be ourselves without seeking validation from others.
Some key takeaways from the book include:
1. The desire to be liked by everyone is a major source of unhappiness.
2. You don't need to be liked by everyone to be happy.
3. Being disliked by others doesn't mean there's anything wrong with you.
4. Embrace your uniqueness and don't try to conform to others' expectations.
5. Take responsibility for your own life and choices.
6. Don't be afraid to express your own thoughts and opinions.
7. You can't control how others think or feel, but you can control how you respond to them.
I think "The Courage to Be Disliked" is a thought-provoking book that encourages readers to embrace their individuality and live a more authentic, fulfilling life.
A judgment one holds as true
In his “The Psychology of Persuasion,” Dr Robert Cialdini laid out six principles of persuasion: reciprocity, scarcity, authority, consistency, liking, and consensus. These principles illuminate the mechanics of persuasion, indicating that we're more susceptible when we perceive a sense of obligation (reciprocity), when rarity is implied (scarcity), when the persuader exudes credibility (authority), when our actions align with past behaviours (consistency), when we harbour positive feelings toward the persuader (liking), and when we observe others following suit. I think persuasion is an intriguing aspect of psychology and it entails guiding someone's beliefs, choices, or behaviours. Failure to engage in independent thinking renders one vulnerable to succumbing to external influences, be they religious, governmental, corporate, or monetary, perpetuating a cycle of ignorance.
Sources of convictions
A stereotype is a social perception that categorises individuals based on their membership in a particular group or their physical attributes. It involves making a generalisation about a group and then attributing those characteristics to individual members of that group. This process simplifies and often distorts the understanding of individuals within the group, potentially leading to biases and discrimination based on preconceived notions rather than individual merit or characteristics. Where do you think these stereotypical beliefs come from?
Why do you think men are better at science than women?
Why do you think overweight people are unhealthy?
Why do you think Muslims are more violent than Christians?
I think by delving into these questions we will prompt reflection on the complex interplay of cultural, historical, and psychological factors that shape our perceptions and attributions of certain traits or behaviours to specific groups. Contact me via e-mail and let’s explore the underlying assumptions and biases that influence your societal perspectives.
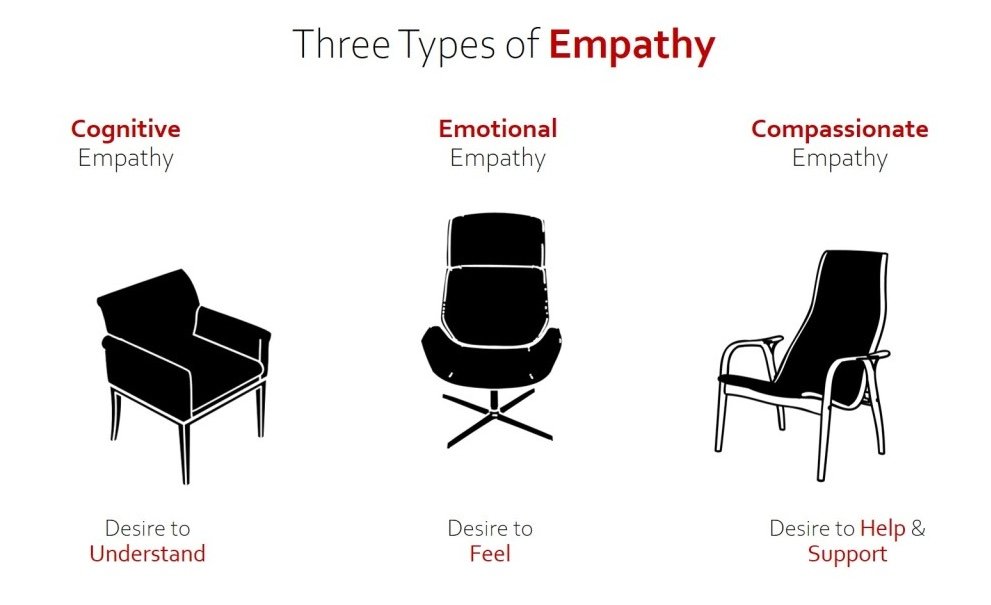
Three forms of empathy
According to psychologists Daniel Goleman and Paul Ekman empathy manifests in three distinct forms: cognitive, emotional, and compassionate.
1. Cognitive empathy is our ability to understand other people’s points of view.
2. Emotional empathy is our ability to respond physically and emotionally to what someone else is experiencing.
3. Compassionate empathy is what creates the bond between team members within an organisation as well as between companies and countries.
I think you can place concentration as the root of empathy, and the importance of the latter in solving individual, personal and general social challenges.